
Meaning Patterns Project: Interpretive Methods
Sense: Our two Sense books and their associated media employ interpretive methods to map out the dimensions of a multimodal grammar, analyzing the role of media, including digital media, in giving shape to our meanings. They use a mixture of the interpretive disciplines of history, philosophy, and social-cultural theory to make an argument about the theoretical notion of “transposition” and its practical applicability.
Related Books:
- Cope, Bill and Mary Kalantzis. 2020. Making Sense: Reference, Agency and Structure in a Grammar of Multimodal Meaning. Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Kalantzis, Mary and Bill Cope. 2020. Adding Sense: Context and Interest in a Grammar of Multimodal Meaning. Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press.
Topic: For this project, choose a topic of interest in an area of human meaning-making. The area could be an aspect of education, but need not necessarily be that. You could choose to look a media (newer digital media or older media), language, image, or one of the other “forms of meaning” that we explore in our two sense books. Look ahead at the topics in these two books for ideas, but also, don’t feel constrained by the topics you find here. Our main reason to have you read these books is to illustrate interpretive methods at work.
Use interpretive methods to explore your chosen topic – in education or any other domain. How do interpretive methods add depth to your understanding of this concept? You may wish to apply interpretive constructs from our transpositional grammar.
Write an interpretive analysis of your topic. Perhaps, if you are in the doctoral program and have in mind possible general topic area, you might choose that. But if you do, in this course, we want you mainly take an interpretive approach to the topic. Even if you finally choose an empirical methodology (e.g. qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods), you are going to need an interpretive part.
If you are worried about choosing a topic, please feel free to run some ideas past us. We mean this to be very open, allowing you to choose something of relevance to your research, or a new area of digital media or education that you would like to explore using interpretive methods.
Word length: at least 3500 words
Project: Your work should contain a methodology section in which you discuss the nature of intepretive methods. This aspect of your peer reviewed project is meta-theoretical, that is you are being asked to develop an account of the theory of interpretive methods – its purposes, possible deployment and the types of analysis that it can generate. If you are a doctoral student, you may (or may not) wish to have your dissertation topic in mind as you write this work. Key questions: What are interpretive methods, in general, or as applied in a mainly interpretive discipline (e.g. history, philosophy, cultural/social theory)? Or, how are interpretive methods operationalized in a meta-analysis? Or how are interpretive methods applied in qualitative or quantitative empirical research?
Your work should then apply principally interpretive methods to your chosen topic. For general guidelines on the peer reviewed project, visit the peer reviewed project pages. * There are two main differences in this course: 1) instead of two main sections, theory > practice, this course suggests two somewhat different sections: interpretive methods theory > interpretative methods application to your chosen topic; 2) we are not offering the learning module option in this course.
When it comes to peer review and self-review, you will be applying the “knowledge processes” rubric that we use in all our LDL courses. Here are some of the ways in which interpretive methods map against this rubric:
Rubric: Use the ‘Knowledge Processes Rubric’ against which others will review your work, and against which you will do your self-review at the completion of your final draft. Below are some of the ways in which interpretive methods map against this rubric:
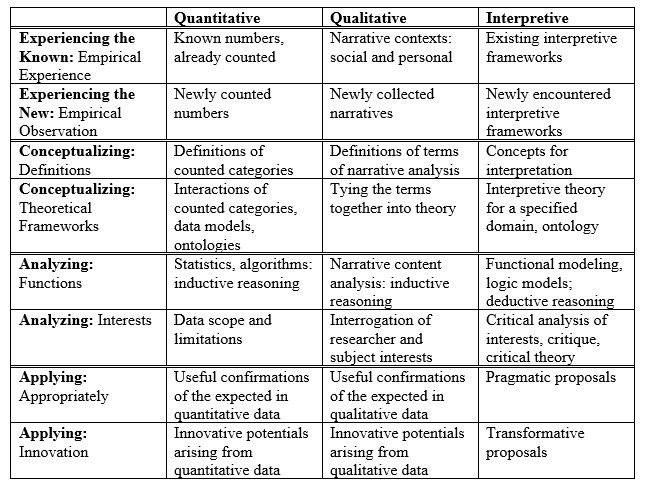
Media: Include media elements, such as images, diagrams, infographics, tables, embedded videos, (either uploaded into CGScholar, or embedded from other sites), web links, PDFs, datasets, or other digital media. Be sure these are well integrated into your work. Explain or discuss each media item in the text of your work. You should refer to specific points of the video with time codes or the particular aspects of the media object that you want your readers to focus on. Caption each item sourced from the web with a link and be sure to cite all media sources in the references list.
References: Include a References “element” or section with the scholarly articles or books that you have used and referred to in the text, plus any other necessary or relevant references, including websites and media.
You should specifically add an asterisk in front of each new scholarly source that you use, considering using at least 5 new sources.